Protein Powder Chocolate Flavour 200gm
200gm Powder in Jar
- Regular price
- Rs. 92.81
- Sale price
- Rs. 92.81
- Unit price
- per
(Inclusive of all taxes)

Prescription Required
Couldn't load pickup availability
Shipping
Free shipping on orders above ₹300, shipped within 2 days of your order.

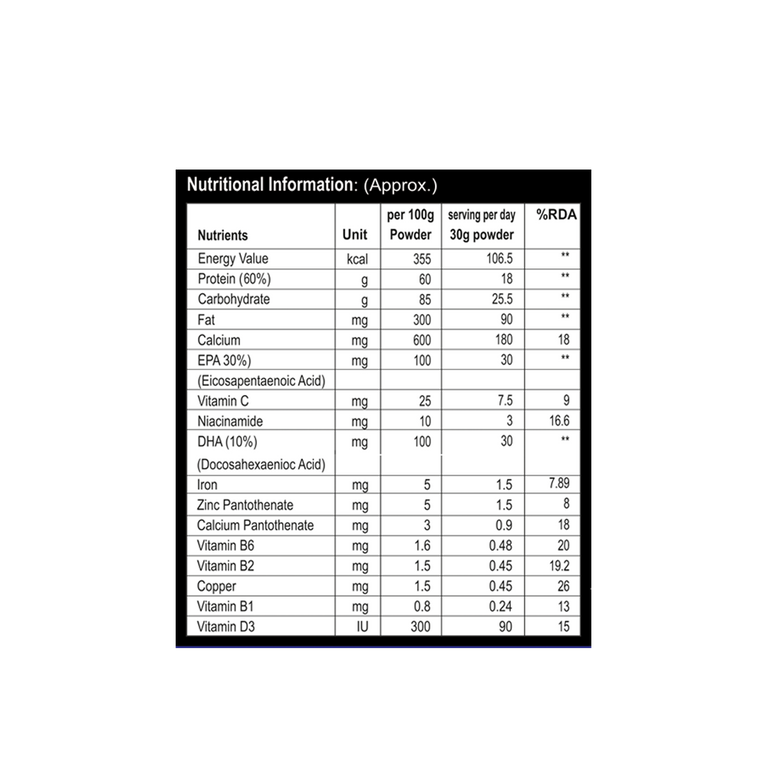

Product Description
Chocolate Protein Powder 200 gm is a flavored nutritional supplement designed to support active lifestyles, providing a convenient source of high-quality protein (typically 20–25 g per serving from whey, soy, or plant-based sources). It aids muscle repair, recovery, and overall protein intake for athletes, fitness enthusiasts, or those with increased needs (e.g., weight management, aging). The chocolate flavor enhances palatability when mixed into shakes, smoothies, or recipes. Not a meal replacement; best as part of a balanced diet. Third-party tested products (e.g., NSF-certified) ensure purity from contaminants like heavy metals.
Use
-
Supplementation to meet daily protein requirements (e.g., 1.6–2.2 g/kg body weight for athletes per ISSN) for muscle maintenance/growth during resistance training
-
Post-workout recovery to support tissue repair and reduce soreness in fitness routines or sports
-
Adjunctive aid for weight management, satiety, or increasing protein in diets for vegetarians/vegans (if plant-based)
-
Not indicated for medical conditions (e.g., malnutrition—use under a dietician's guidance); not a substitute for whole foods
How it works
Protein powder delivers essential and branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs: leucine, isoleucine, valine) that serve as building blocks for muscle protein synthesis (MPS):
-
Upon ingestion, proteins are hydrolyzed into amino acids during digestion (absorption in 1–2 hours for whey; slower for casein/plant sources), entering the bloodstream for uptake by muscles.
-
Exercise-induced micro-tears in muscle fibers trigger inflammation and repair; leucine (2–3 g/serving in whey) activates the mTOR signaling pathway, stimulating MPS to rebuild stronger tissue (e.g., 20–30% MPS increase post-exercise per studies).
-
Fast-digesting types (e.g., whey isolate) provide rapid amino acid delivery during the "anabolic window" (0–2 hours post-workout), while blends offer sustained release. Overall, it supports net protein balance, but efficacy depends on total intake, training, and calories—not standalone for gains.
Benefits
-
Muscle support: Increases MPS by 25–50% when combined with resistance training, aiding lean mass gains and recovery.
-
Satiety and weight control: High protein promotes fullness, reducing calorie intake by 10–15% and supporting fat loss while preserving muscle.
-
Energy and convenience: Provides sustained fuel for workouts/daily activities; easy to incorporate for busy lifestyles or those struggling with whole-food protein.
-
Versatility: Chocolate flavor masks taste in recipes; suitable for various goals.
How to use
Each serving provides a robust dose of protein to support muscle repair and growth, making it an excellent choice for athletes and fitness enthusiasts. Dose should be directed by your dietician or healthcare professional. Mix well in water or milk, whether you use a shaker bottle or a blender to ensure a smooth, lump-free consistency every time.
Side Effects
Common side effects (mild and infrequent; <5% users):
-
Digestive: Bloating, gas, cramping, diarrhea (from lactose in whey concentrates or FODMAPs in plant proteins)
-
Allergic: Rash, itching, hives (e.g., dairy/soy sensitivity)
Less common/rare but serious side effects (seek medical attention):
-
Weight gain: If caloric surplus (e.g., added sugars in flavored powders)
-
Nutrient imbalance: Over-reliance may displace vitamins/minerals from whole foods
-
Renal strain: Dehydration or high intake (>3 g/kg) in those with pre-existing kidney disease (e.g., elevated creatinine)
-
Other: Acne flare-ups (anecdotal link to dairy/IGF-1); heavy metal exposure (rare in untested products)
Most resolve with dose adjustment or switching types (e.g., isolate for low-lactose); hydrate well (2–3 L/day).
Safety Advice
-
Select reputable brands with third-party testing (e.g., NSF/USP for contaminants like lead/arsenic); check labels for allergens (dairy, soy) and added sugars (<5 g/serving ideal).
-
Use as a supplement, not replacement—aim for 70–80% protein from whole foods (e.g., eggs, nuts, legumes) to ensure micronutrients/fiber.
-
Consult a doctor/dietician before use if pregnant, breastfeeding, or with conditions (e.g., kidney/liver disease); monitor intake to avoid excess (RDA 0.8 g/kg for adults, higher for athletes).
-
If digestive issues occur (e.g., bloating from whey), switch to hydrolysate, isolate, or plant-based (e.g., pea/rice). Stay hydrated; avoid if history of allergies. Not for children <18 without guidance.
Storage Conditions
Store at a temperature below 86°F (30 °C). Protect from light and moisture.
FAQs
Is chocolate protein powder safe to use every day?
Yes, when part of a balanced diet and within limits (1–2 servings/day); it supports protein needs without harm for healthy adults. Consult a doctor if you have kidney/liver issues, as excess (>2.2 g/kg) may strain organs.
Can protein powder cause acne?
Possibly in sensitive individuals, dairy-based whey may elevate IGF-1, increasing sebum and acne. Switch to plant-based or isolate if noticed—evidence is correlational, not causal.
Is it better to drink a protein shake before or after a workout?
Post-workout (within 1–2 hours) optimizes recovery, but total daily intake matters more than timing. Pre-workout (30–60 min) can provide energy if fasted.
What is the difference between protein powder and whey protein?
Whey is a specific type of protein powder (milk-derived, fast-absorbing, high in BCAAs); general protein powders include whey, casein (slow-digesting), or plant-based (e.g., pea/soy for vegans, complete amino profiles in blends).
Can I replace meals with a protein shake?
Occasionally, yes, but not long-term—add fruits, veggies, fats (e.g., nut butter) for balanced macros/micronutrients. Over-reliance risks deficiencies (e.g., fiber, vitamins); whole foods are preferred for gut health.
How do I know which protein powder is safe?
Choose certified products (NSF, Informed-Sport, USP) tested for purity/label accuracy. Avoid proprietary blends; check for allergens, low heavy metals (<0.5 mcg/g lead per Prop 65), and minimal additives.
How many scoops should I have per day?
1–2 scoops (20–50 g protein) typically suffices, based on needs (e.g., 1.6 g/kg for athletes). Calculate total from diet—supplement gaps, not exceeding 2.2 g/kg to prevent GI/kidney issues.
 Manufacturer Name:
Manufacturer Name: Scythian Healthcare
 Marketed by:
Marketed by: First Remedy Pharmacies Private Limited
The information provided on this website is for general informational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult with a physician or qualified healthcare provider for any medical concerns. Never disregard professional advice or delay seeking it based on the information you read here.




